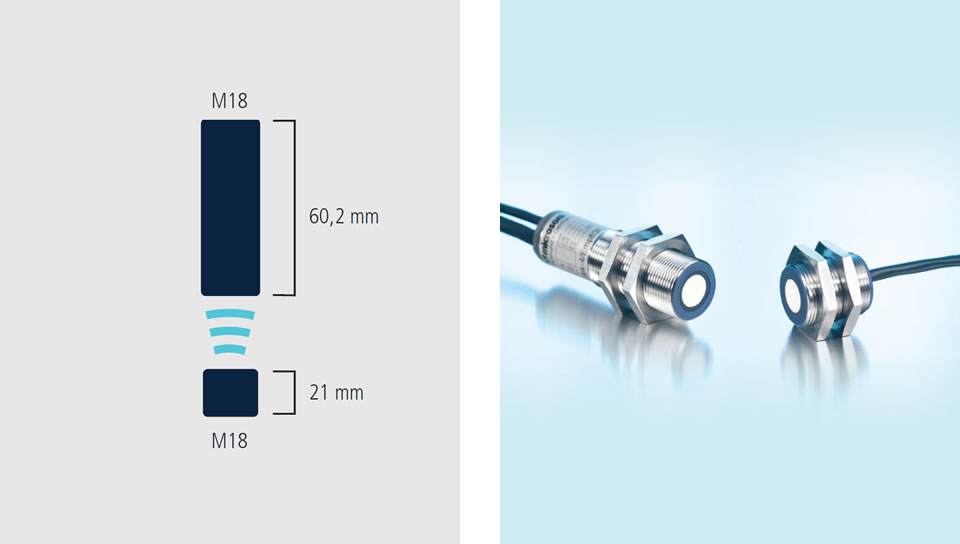
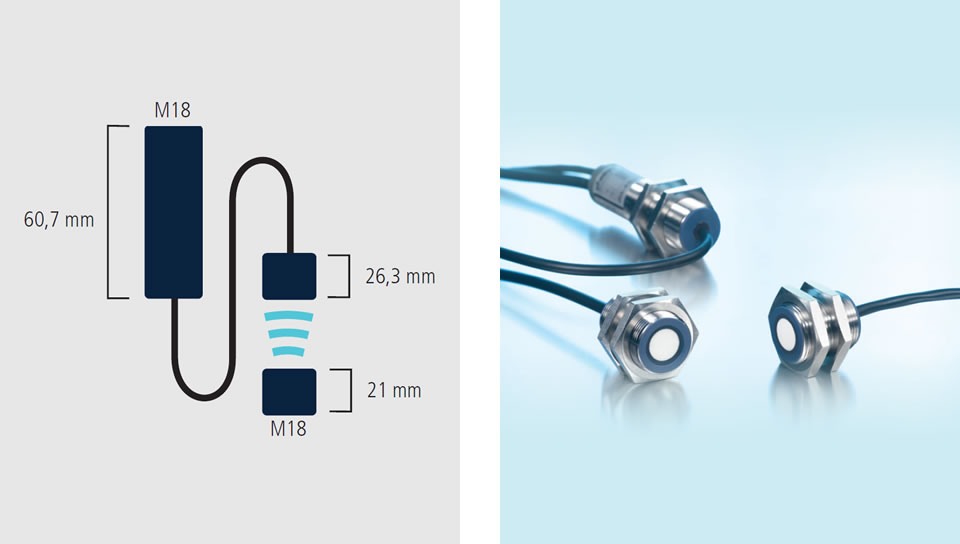
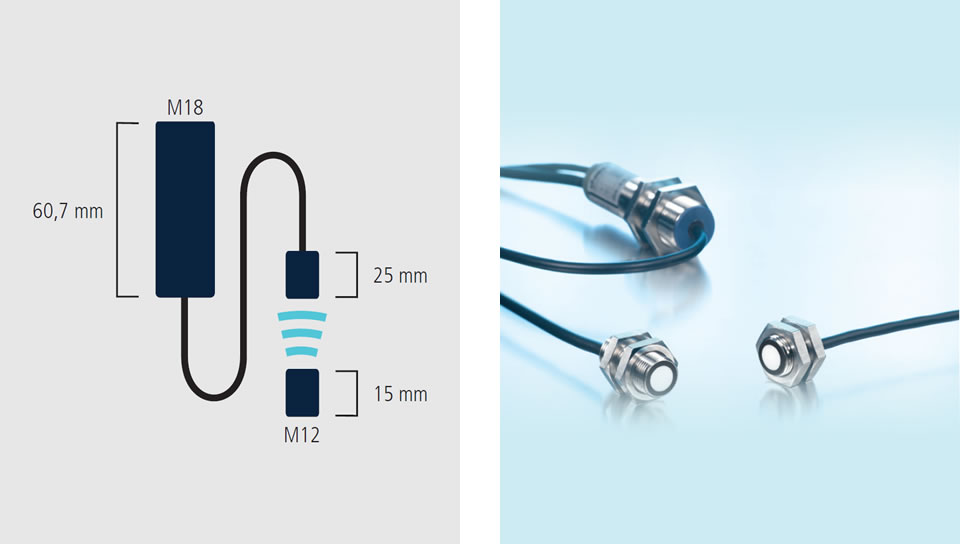
The task
of double-sheet control is to identify two or more pieces or sheets inadvertently adhering together.
The functional principle
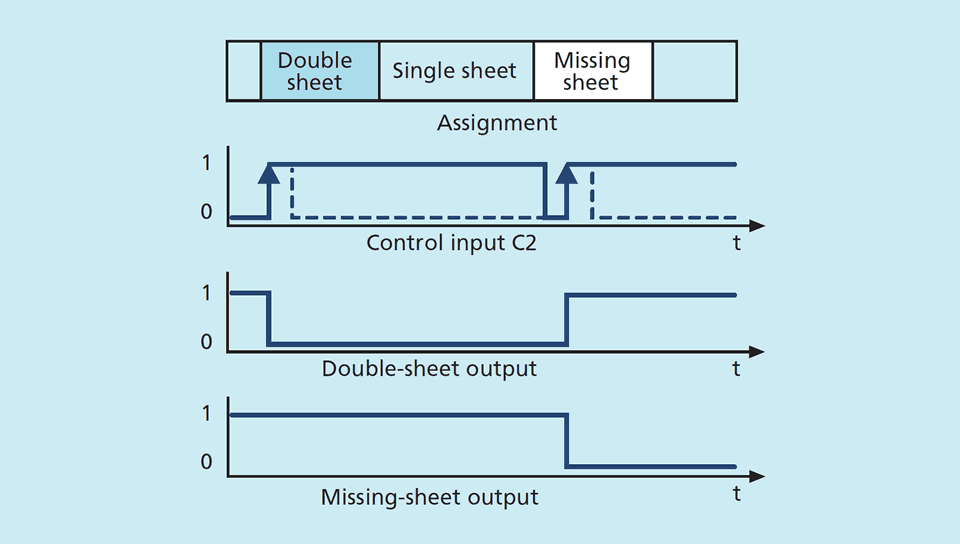
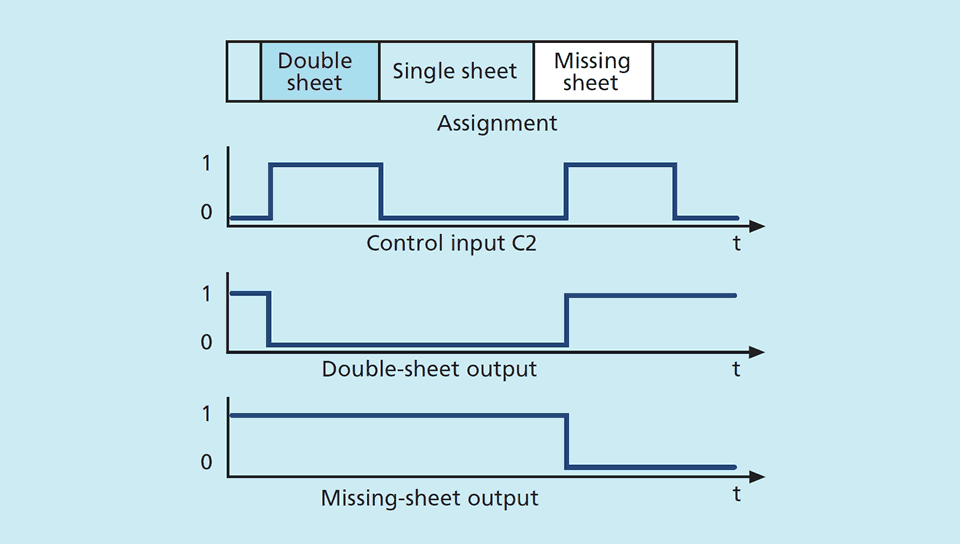
A high-frequency ultrasonic transmitter beams against the sheet from the underside. The beamed signal induces the material to vibrate. The effect of these vibrations is a very small sonic wave on the other side of the sheet being spread. This wave is evaluated by the ultrasonic receiver on the opposite side. The signal from the stacked sheet ("double sheet") is so weak that it hardly gets to the receiver. The dbk+4 detects missing, single and double sheet.
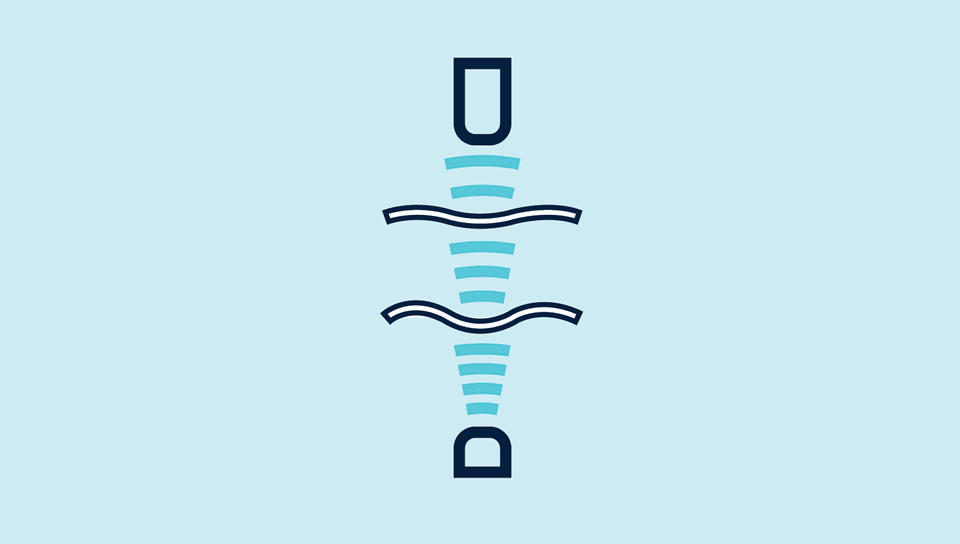
Functional principle
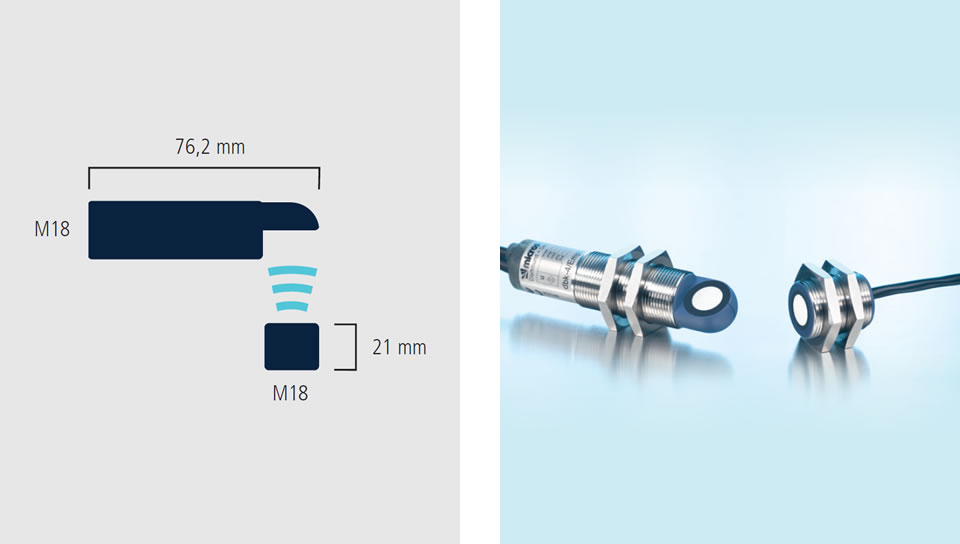
The working ranges
The new dbk+4 has 3 control inputs by means of which 3 working range can be preselected. The standard working ranges covers the sheet material weight range from 20 g/m2 to 1,200 g/m2. Extremely thin materials such as Bible printing paper with a weight per unit area of less than 20 g/m2 are scanned with the use of the "Thin" setting.
The "Thick" setting is available for paperboard containers and fine-corrugated card. Changes between the working ranges can be undertaken under on-going operations. A Teach-in for the material to be scanned is not necessary.
If the 3 control inputs stay unconnected, then the dbk+4 operates in the standard working range. As such, a very broad material spectrum can be scanned.
Teach-in
The Teach-in function is additionally available for materials which cannot be scanned with one of the three working ranges. A material Teach-in is done by inserting a single sheet into the double-sheet control. The C3 control input is then placed to logic 1 level for at least 3 seconds. Materials with non-homogeneous elements must be moved during the Teach-in phase so that the dbk+4 detect them. Success with a Teach-in operation is shown by a green LED. The material can now be scanned. The Teach-in makes it possible to scan material from thin Washi to wafers glued with a water film.
Range of uses of dbk+4:
- Assembly machines
- Battery cell production
- Folding machines
- Labelling
- Manufacturing of solar cells and silicon wafers
- Paper-processing machines
- PCB manufacturing
- Sheet-printing machines